In our technology-driven world, the demand for power is unending. From the remote controls scattered around our living rooms to the emergency torches tucked away in drawers, batteries remain an essential part of our daily lives. And while the shift towards rechargeable batteries is noticeable, there's a stalwart player that continues to hold its ground for both its economic and sustainable stature – the alkaline battery.
In the age of rechargeable batteries and ever-increasing power demands, the humble alkaline battery might seem like a relic. But don't be fooled! Alkaline batteries are still a fantastic choice for many devices, offering a balance of affordability and long-lasting power that shouldn't be ignored.

Understanding the Basics: What are Alkaline Batteries and How Do They Work?
Alkaline batteries are a type of primary battery dependent on the reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide (Zn/MnO2). Characterised by their long shelf life and higher energy density, alkaline batteries have dominated portable devices since their mainstream adoption.
The chemistry behind alkaline batteries is fascinating and sets them apart from other battery types. When the battery is in use, the zinc (Zn) within the anode reacts with the manganese dioxide (MnO2) in the cathode, facilitated by an alkaline electrolyte, usually potassium hydroxide (KOH). This reaction releases energy, powering your devices. The alkaline solution used is key to the batteries' performance, offering a steadier energy output and longer life span compared to the acidic electrolytes found in older battery technologies.
Alkaline batteries first made their debut in the 1950s, introduced by the Eveready Battery Company (now known as Energizer). The innovation was aimed at providing consumers with a more durable and reliable power source for their everyday devices. Over the decades, improvements in the manufacturing process and materials have further enhanced their energy density and overall performance, cementing alkaline batteries' status as the go-to choice for a wide range of household items.
The Green Side of Alkaline: Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Contrary to popular belief, alkaline batteries have made strides towards environmental sustainability. Most modern alkaline batteries are mercury-free, reducing their environmental impact compared to older models. Plus, their long shelf life means fewer replacements, leading to less waste over time.
However, the path to sustainability doesn't end with the reduction of hazardous materials. Alkaline batteries still pose environmental challenges when disposed of improperly.
Recognising this, various recycling programs and initiatives have been established globally to tackle the issue. In the United States, for example, the Call2Recycle program offers a convenient way for consumers to recycle their used alkaline batteries responsibly. This not only helps in diverting potentially harmful materials from landfills but also recovers valuable metals that can be reused in manufacturing new products.
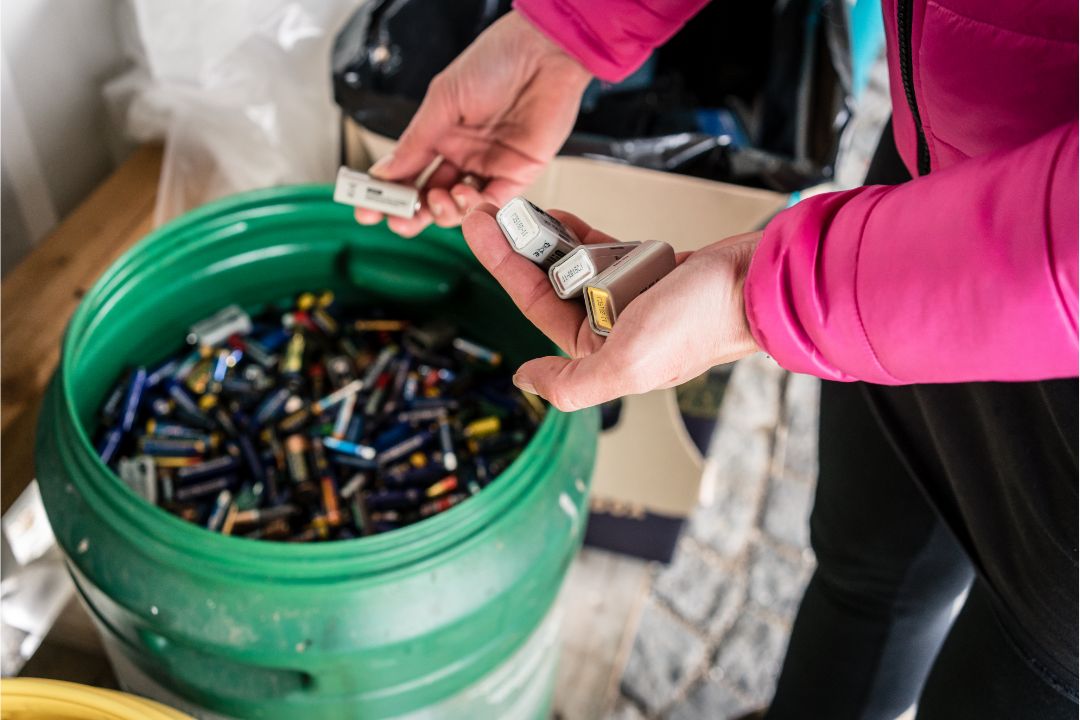

Here in New Zealand, recycling schemes have been gaining traction as part of the effort to mitigate the environmental impact of waste, including alkaline batteries. The Battery Industry Group (BIG) plays a pivotal role in this initiative, offering guidelines and support for battery recycling across the country. They collaborate with municipalities and private entities to increase accessibility to recycling programs, ensuring that consumers have convenient options for disposing of their alkaline batteries responsibly.
Notably, the Rechargeable Battery Recycling Corporation (RBRC) program in New Zealand has set up numerous drop-off locations nationwide, making it easier for New Zealanders to contribute to a more sustainable environment by recycling their used batteries. These efforts are crucial for reducing landfill waste and preventing the leakage of hazardous substances into ecosystems, aligning with New Zealand's broader environmental sustainability goals.
Additionally, some manufacturers, including Energizer, and retailers have taken it upon themselves to create take-back programs, encouraging users to return spent batteries for proper disposal or recycling, further reducing the environmental footprint of alkaline batteries. With these efforts, the aim is to foster a more circular economy where battery materials are efficiently recycled and reused, minimising waste and environmental impact.
The Economic Advantage: Why Alkaline Batteries Can Be a Budget-Friendly Choice
When it comes to powering your devices, initial cost and total value are key considerations. Alkaline batteries shine brightly in both aspects. They offer a compelling average cost per watt-hour and their performance in low-drain devices rivals that of many rechargeables, providing an attractive option for budget-conscious consumers who still seek quality and reliability.
Alkaline batteries not only present a cost-effective choice for consumers but also deliver dependable performance across a wide range of applications. They are the go-to power source for countless everyday devices, including remote controls, torches, and digital clocks, where their longevity in low-drain situations can be particularly advantageous. This durability, coupled with their affordability, means that for many households and businesses, alkaline batteries provide an excellent balance between quality and cost.
Furthermore, the ability of alkaline batteries to maintain their charge for extended periods when not in use makes them an ideal choice for emergency kits or infrequently used devices, ensuring that when the need arises, they're ready to perform. This blend of reliability, versatility, and value solidifies their status as a staple in the realm of battery-powered technology.
Real-World Applications: Where Alkaline Batteries Excel
Alkaline batteries are the unsung heroes for low-drain devices such as smoke detectors, remote controls, and clocks. Their ability to offer consistent power over extended periods makes them ideal candidates for emergency kits, where long-term reliability is non-negotiable. Plus, their universal availability ensures you're never caught powerless in a pinch.
Alkaline batteries come in a variety of sizes and capacities to meet the diverse demands of modern electronic devices. Each type is designed for specific applications, from small gadgets to larger, more power-intensive equipment:
- AA: The most common size, ideal for everyday devices like remote controls, wireless mice, and small flashlights.
- AAA: Smaller than AA, these are perfect for devices that require compact power sources such as TV remotes, portable speakers, and digital cameras.
- C and D: Larger and designed for higher power needs, these are used in toys, boomboxes, and emergency equipment like flashlights and portable radios.
- 9V: Often found in smoke detectors, carbon monoxide alarms, and professional audio equipment, providing reliable power for safety and performance.
Each of these types offers the reliability and longevity alkaline batteries are known for, ensuring that devices operate efficiently and effectively, regardless of their power requirements.
Tips for Maximising the Longevity of Alkaline Batteries
To get the most out of your alkaline batteries, store them in a cool, dry place to extend their shelf life. Also, be mindful to remove batteries from devices not in use for extended periods to prevent leakage and damage.
Additionally, consider pairing batteries of the same brand, capacity, and age to avoid imbalances that can lead to premature depletion. Regularly check the battery compartment of your devices for signs of corrosion or leakage, as this can affect performance and may cause damage.

Finally, investing in a good battery tester can help you distinguish between fully charged, partially used, and depleted batteries, ensuring you only replace what is necessary and potentially extending the overall life of your battery stock by preventing unnecessary waste.
It's important to note that while alkaline batteries boast an impressive shelf life, they are not rechargeable. Once depleted, they must be properly disposed of and replaced. This characteristic differentiates them from other types of batteries, such as NiMH or lithium-ion, which can be recharged and used multiple times. For devices that are used frequently, investing in rechargeable batteries may be a more economical and environmentally friendly option.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of Alkaline Batteries in a Sustainable, Tech-Driven World
Despite the growing prominence of rechargeable alternatives, alkaline batteries maintain a significant role in our digital age. Their balance of affordability, performance, and sustainability ensures their continued relevance. For eco-conscious consumers, tech enthusiasts, and budget-savvy shoppers, alkaline batteries represent a practical solution that aligns with both their ethical values and economic considerations.
By understanding when and how to use these power sources effectively, consumers can enjoy long-lasting, sustainable power on a budget. Alkaline batteries, with their blend of efficiency and accessibility, affirm that sometimes, the classic choice remains a great choice.
Remember, the key to powering our devices smartly lies in making informed choices that consider the environment, our wallets, and our needs. Alkaline batteries, with their surprising array of benefits, offer just that. Shop Alkaline batteries at Ivent.